Release date: 2017-12-22
On December 21, Chongqing Daily reporter learned from the Xinjun Hospital of the Army Military Medical University that the Zheng Hongting team of the Department of Endocrinology of the hospital discovered for the first time in the world that the hypoglycemic agent DPP-4 inhibitor (ie, the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor) can not only It plays a role in regulating blood sugar, and can also significantly promote wound repair in diabetic patients, shortening the healing time, and this effect is independent of its hypoglycemic effect.
The discovery was published in the international journal Diabetes, the top journal of diabetes research. The first author of the thesis is Associate Professor Long Min and graduate student Cai Leiqin.
According to Zheng Hongting, diabetic patients are prone to various complications such as blood vessels and nerves due to skin histology and physiology changes, vascular neuropathy and infection. Once a skin-damaged wound is formed, the patient's own high-sugar level of the body often makes Inflammatory cell chemotaxis and phagocytosis are reduced, bacteria are not easily removed, and wounds are difficult to heal. In clinical practice, the most common is that diabetic patients form diabetic foot due to long-term difficulty in healing the wound of the foot, and severe amputation may occur.
Through previous research, Zheng Hongting found that DPP-4 inhibitors, as a classic oral hypoglycemic agent, are widely used in the treatment of diabetes, but they may have positive or negative effects on diabetic complications in addition to hypoglycemic effects. On this basis, the research team further found through experiments on ex vivo cells and mouse carriers that DPP-4 inhibitors can enhance the migration of skin epithelial cells through direct and indirect effects, promote wound repair and accelerate the healing of diabetic ulcers. . In addition, DPP-4 inhibitors can reduce collagen synthesis and deposition and improve scar formation in diabetic ulcers.
The team then extended this research to clinical trials, and the results of randomized clinical trials in 67 patients with type II diabetic foot also confirmed that conventional oral DPP-4 inhibitors not only play a role in hypoglycemic, but also contribute to diabetic wounds. heal. This study provides new evidence for the clinical application of DPP-4 inhibitors in the future.
Zheng Hongting said that the study has achieved a deep integration of basic and clinical, and will promote the in-depth and promotion of the field of metabolic disease translation medicine research.
Source: Chongqing Daily
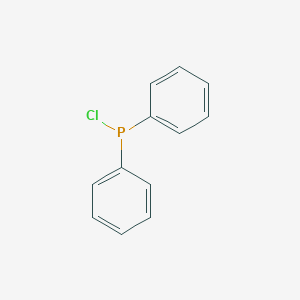
Chlorodiphenylphosphine CAS No.1079-66-9
Chlorodiphenylphosphine Basic Information
Product Name: Chlorodiphenylphosphine
CAS: 1079-66-9
MF: C12H10ClP
MW: 220.63
EINECS: 214-093-2
Mol File: 1079-66-9.mol
Chlorodiphenylphosphine Structure
Melting point 14-16°C
Boiling point 320 °C(lit.)
density 1.229 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
storage temp. Store at R.T.
solubility Miscible with alcohol. Slightly miscible with ammonia.
form Liquid
color Colorless to yellow
Water Solubility Reacts violently
Sensitive Air & Moisture Sensitive
Chlorodiphenylphosphine Application
Chlorodiphenylphosphine is used to introduce the diphenylphosphinyl moiety by aryl ortho-lithiation. It is also used as an intermediate to make antioxidants, flame retardants, stabilizers, Catalysts, photoinitiators, and optical brighteners. Used as a halogenation reagent for the conversion of alcohols into halides, in the preparation of solid-phase reagent for the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides.
Chlorodiphenylphosphine,Chlorodiphenylphosphine Oxide,Chlorodiphenylphosphine 31P Nmr,Chlorodiphenylphosphine Synthesis
Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com