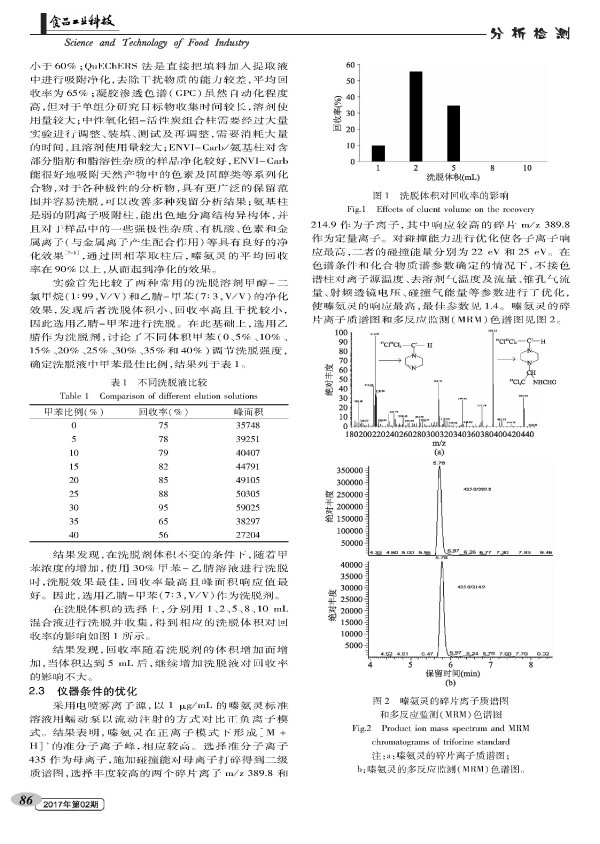
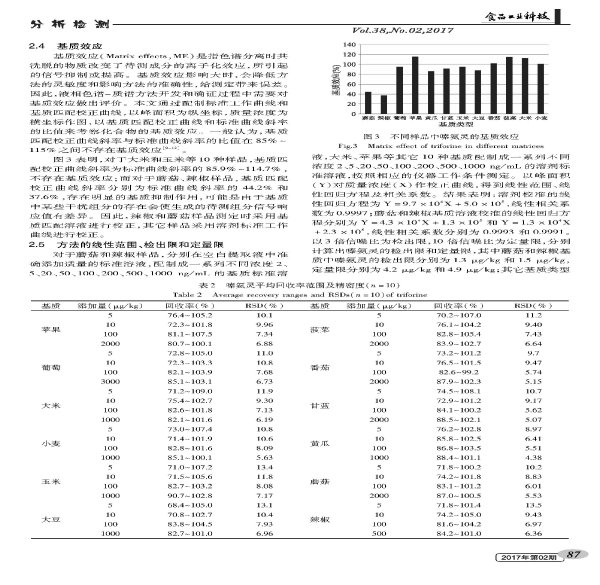
Azinamide is an amide-based systemic fungicide widely used in the control of ***, rust and scab in cereals, fruit trees and vegetables. Because it can destroy red blood cells in animals, many countries have strict regulations on its maximum residue limit; the EU has strictly established the maximum residue of 505 kinds of foods, the most stringent, the range is 0.01-0.05 Mg/kg; Japan stipulates the maximum residue of oxazinamide in 193 kinds of foods; China GB2763-2014 "Food Safety National Standards for Pesticide Residues in Foods" only stipulates the limit requirement of oxazinamide in 17 kinds of foods. No matter the type of samples involved or the residue standards are much lower than those of developed countries and international organizations, there are hidden dangers in China's food safety problems. With the tightening of trade technology measures in various countries, the number of monitoring substrates has increased greatly, and the current testing methods have been unable to meet the EU's maximum requirements of nearly 70%.
At present, research at home and abroad focuses on simple matrices of rice, cucumber and watermelon. Studies on vegetables, beans and edible fungi have not been reported. The detection methods mainly include gas chromatography, high performance liquid chromatography, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, and the like. Pretreatment with gas chromatography is cumbersome. The sample needs to be derivatized, which takes a long time and is prone to false positive results. High performance liquid chromatography and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry have low sensitivity and poor selectivity and specificity, which can not meet the needs of detection work. In this paper, the extraction and purification of samples were optimized with reference to internal or external literature methods. According to the requirements of domestic and international residues of oxazinamide, several representative substrates such as grains, beans, fruits, vegetables and edibles were selected. As a detection object, the method of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry was used as an analytical method to establish a method for detecting the residual amount of oxazinamide in plant-derived foods. The method is simple, rapid, and sensitive, and can meet the increasingly stringent pesticide residues in the world. Testing requirements.