In order to implement the spirit of the National Health and Wellness Conference, establish a higher quality medical service system, build a healthy Shenzhen, build a medical and health highland, and build an international medical center to enable the public to enjoy a higher level of medical services, according to the National Health Service. System Planning Outline (2015-2020), Notice of the National Health and Family Planning Commission on Printing and Distributing Medical Organizations Planning Guidelines (2016-2020), and Guangdong Provincial People's Government's Plan for Printing and Distributing Guangdong's Medical and Health Service System (2016) - 2020) and the "13th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development of Shenzhen", "Implementation Opinions of the Shenzhen Municipal People's Government on Deepening the Reform of the Medical and Health System and Building a Strong Health City", "Shenzhen Health This plan is specially formulated with the Health 13th Five-Year Plan.
First, the planning background
(1) Analysis of the status quo.
During the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan†period, the total medical resources of the city increased steadily, the medical service system continued to improve, the service accessibility continued to improve, and the regional health development imbalance gradually improved.
1. The status of medical resources.
In 2015, there were 3561 medical and health institutions in the city, including 125 hospitals, 613 community health service centers (hereinafter referred to as social health centers), 10 maternal and child health centers, and 8 specialized disease prevention and treatment centers. The city can supply 38,132 beds, including 35,353 hospitals, 2,367 Maternal and Child Health Hospitals, and 280 specialist hospitals. There were 29,007 practicing (assistant) physicians and 31,715 registered nurses in the city. The number of beds per 1,000 permanent residents is 3.4, the number of practicing (assistant) doctors per thousand permanent residents is 2.6, and the number of nurses per 1,000 permanent residents is 2.80. According to the fifth National Health Service Survey, 95.75% of the city's families can reach the nearest medical institution within 15 minutes.
2. Medical service utilization and demand status.
In 2015, the city's medical and health institutions completed 890,500,700 person-times, including 71,170,100 hospitals, 6,241,800 women and children's hospitals, 1,140,000 specialist hospitals, and 4,707,200 outpatients. The clinic has 4.5759 million person-times. In the year, 1,240,700 inpatients were admitted. The hospital bed utilization rate in the city was 84.0%, of which the municipal hospitals reached 95.1%. The average hospital stay for medical institutions was 7.9 days. According to the fifth national health service survey, the prevalence of residents in our city for two weeks was 27.85%, an increase of 5.8 percentage points from the previous survey.
3. Residents' health status.
During the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan†period, the main health indicators of residents in the city were ranked first in the country. The average life expectancy of residents increased from 78.01 years to 80.66 years old, and the maternal mortality rate dropped from 15.41/100,000 to 5. 3/100,000, the infant mortality rate dropped from 2.35‰ to 1.83‰.
(2) There are problems.
1. The total amount of medical resources is insufficient.
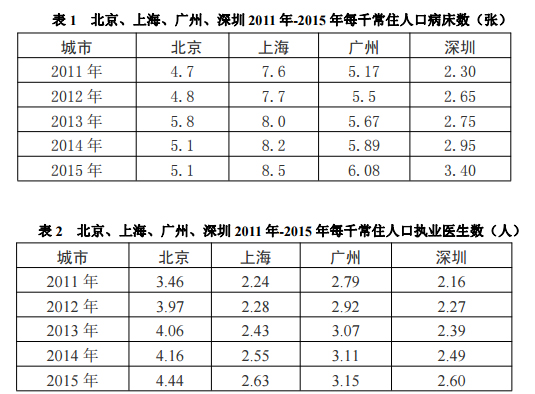
In general, the total amount of medical resources in the city, especially high-quality resources, is relatively insufficient, and the pressure on medical services is large, making it difficult to meet the rapidly growing demand for medical services for residents. In 2015, the number of beds per 1,000 permanent residents in the city was 3.4, lower than the national average of 5.1 and the average of 4.02 in Guangdong Province, ranking second in the Pearl River Delta region; practicing for every 1,000 permanent residents (Assistant) 2.6 physicians and 2.80 registered nurses. The above indicators have a large gap compared with Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou (see Table 1, Table 2). With the improvement of the level of economic and social development and the improvement of the social security system, the rigid demand for medical treatment by the masses has been rapidly released, and the contradiction between the rapid growth of health demand and the insufficient supply of services still exists.
2. Medical resources are not properly allocated and utilized.
The medical resources of our city are unevenly distributed outside the original special zone and within the special zone. As the resident population continues to increase and the floating population changes constantly, the imbalance of such resource allocation will gradually become more prominent. Medical resources are relatively concentrated in the central urban area. With the change of industrial structure, the population will gradually spread to the outer city, the proportion of the population in the central city will gradually decrease, and the supply and demand of medical resources will become increasingly imbalanced. Due to many factors in the past, the existing medical resources in the four eastern districts and other districts are obviously insufficient. The grading diagnosis and treatment system is imperfect, the allocation of medical and health resources is unreasonable, the utilization rate is not high, the capacity of primary health care institutions is not strong, the division of labor coordination mechanism between hospitals and social welfare centers is imperfect, and the problems of overcrowding in large hospitals and idle resources of small social resources are simultaneously exist.
3. The integrated grading medical service system needs to be improved.
The functional orientation of medical institutions is not clear enough, and some different levels and different types of medical institutions have disorderly competition. The fragmentation of the medical service system is more prominent, and the effective communication between medical institutions is insufficient. The cooperation between medical institutions at all levels is not smooth and the coordination is not strong. The grading diagnosis and treatment mode of the first-level primary consultation, two-way referral, rapid division and treatment, and up-and-down linkage needs to be improved.
Our organic vegetable powder mainly used dehydration technology. Dehydration vegetable powder remained most fiber and taste of fresh vegetables, so they are suitable to be added in sauce, stuff, pudding, yogurt and dessert. Some vegetable powder could be applied as pigment like red beet root powder. Some could be mixed with other super green powders to make health formula, kale powder and broccoli powder are always good choice for customers.
Vegetable Powder,Red Beet Root Powder,Broccoli Powder,Organic Vegetable Powder
YT(Xi'an) Biochem Co., Ltd. , https://www.ytwholefood.com